Headless CMS vs Traditional CMS: A Quick Guide to Pick Your Best Fit
In today’s digital landscape, managing and delivering content efficiently is crucial for businesses. Content Management Systems (CMS) play a vital role in helping organizations create, organize, and publish content.
However, there are different types of CMS available, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Two popular options are Headless CMS and Traditional CMS.
In this article, we will explore the differences between these two approaches and help you determine which one is the best fit for your needs.
What is a Headless CMS?
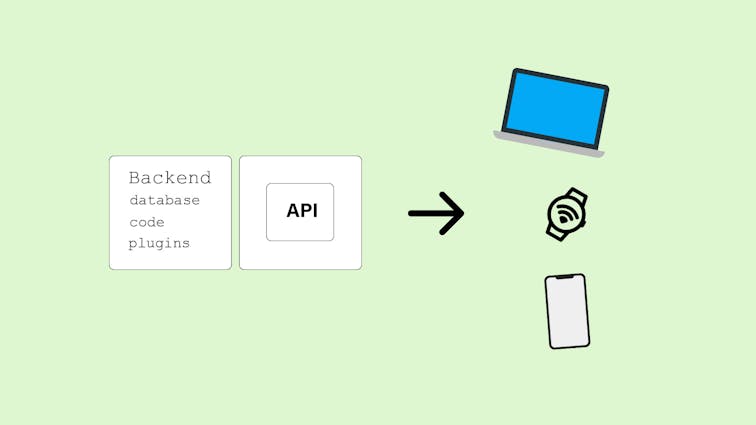
A Headless CMS, as the name suggests, is a CMS without a frontend “head” or presentation layer. It focuses solely on content creation, management, and storage, separating the content from its presentation.
With a Headless CMS, the content is stored in a central repository and can be accessed through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), allowing it to be delivered to various platforms and devices.
Example: Contentful, Strapi, Ghost
What is a Traditional CMS?
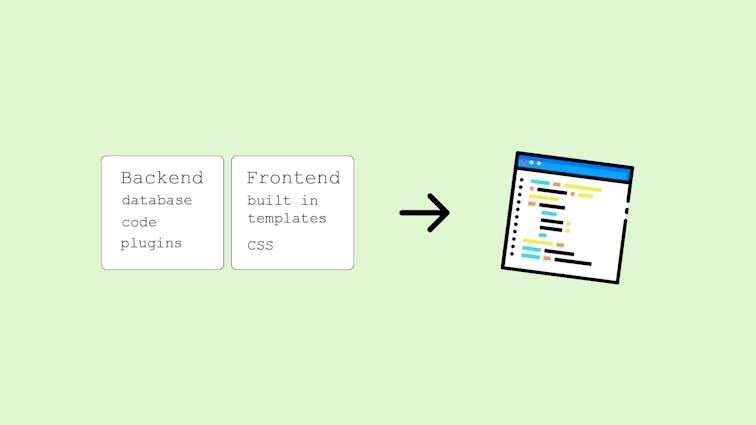
A Traditional CMS is an all-in-one solution that combines content creation, management, storage, and presentation in a single system.
It provides a user-friendly interface for content editing and typically includes templating and theming capabilities for designing the frontend.
The content and presentation are tightly coupled in a Traditional CMS, meaning the same system handles both aspects.
Example: WordPress, Drupal, Joomla
Key Differences between Headless CMS and Traditional CMS
1. Architecture
The architecture is one of the fundamental differences between Headless CMS and Traditional CMS. A Headless CMS follows a decoupled architecture, where the frontend and backend are separate entities.
The backend is responsible for content management, while the frontend can be developed independently using any technology stack. In contrast, Traditional CMS has a monolithic architecture, where the frontend and backend are tightly integrated.
2. Content Presentation
In a Headless CMS, content can be presented on multiple channels and devices, such as websites, mobile apps, smartwatches, or even IoT devices.
The separation of content and presentation allows for greater flexibility and adaptability to different user interfaces.
On the other hand, a Traditional CMS is primarily focused on delivering content for a specific frontend, usually a website.
The presentation layer is tightly integrated with the CMS, making it less flexible when it comes to delivering content to various platforms.
3. Flexibility and Scalability
Headless CMS offers a high level of flexibility and scalability. Since the frontend is decoupled, you have the freedom to choose any technology stack, programming language, or framework to build your frontend applications.
This flexibility allows for more creativity and customization in designing the user experience. Additionally, headless architectures are highly scalable as they can handle increased traffic and user interactions more efficiently.
In contrast, Traditional CMS platforms may have limitations when it comes to customization and scalability, as they are designed with specific templates and themes.
4. Development Speed
When it comes to development speed, Traditional CMS platforms often have an advantage. They provide a comprehensive set of tools and pre-built templates, making it easier and quicker to set up a website or application.
With a Traditional CMS, you can leverage the built-in features and functionalities without having to build everything from scratch.
However, in a Headless CMS, the development process may take longer as you have to create the frontend from scratch using your preferred technology stack. This allows for more flexibility but requires more development effort.
5. Content Delivery
Headless CMS excels in content delivery across multiple channels and devices. With the help of APIs, content can be easily distributed and consumed by various applications and platforms.
Whether it’s a website, a mobile app, or a smart device, the content can be seamlessly delivered and updated in real-time.
Traditional CMS platforms, on the other hand, are primarily focused on delivering content for a specific frontend. While some Traditional CMS platforms offer APIs for integration, they may not be as robust and versatile as those provided by Headless CMS.
Pros and Cons of Headless CMS:
Pros
- Flexibility to deliver content across multiple platforms and devices.
- Freedom to choose any frontend technology stack.
- Scalability to handle increased traffic and user interactions.
- Easy integration with third-party services and APIs.
- Improved security as the backend is separated from the frontend.
Cons
- Higher development effort required to build the frontend.
- Limited out-of-the-box features compared to Traditional CMS.
- Potential complexity in managing multiple systems and integrations.
- Content preview and editing may require additional setup and tools.
Pros and Cons of Traditional CMS
Pros
- Quick and easy setup with pre-built templates and themes.
- Comprehensive set of features and functionalities out of the box.
- Simplified content editing and preview within the same system.
- Lower development effort required for frontend implementation.
Cons
- Limited flexibility to deliver content to multiple platforms.
- Dependency on the CMS provider for updates and new features.
- Potential scalability issues with high traffic or complex requirements.
- Less freedom in choosing frontend technology stack and design.
These are just a few key points to consider when evaluating Headless CMS and Traditional CMS for your projects. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on your specific needs, goals, and preferences.
While Headless CMS offers greater flexibility, scalability, and cross-platform content delivery, it also requires more development effort and relies on successful integrations.
Traditional CMS, on the other hand, may be a quicker and more user-friendly solution, but may have limitations in terms of customization and compatibility with multiple platforms.
Take the time to carefully analyze your project requirements and choose the right CMS according to your unique needs to ensure a successful and well-optimized content strategy.
In some cases, you might even find it beneficial to implement a hybrid approach, combining aspects of both Headless and Traditional CMS systems to suit your particular project and organization demands.
**Choosing the Right CMS for Your Needs **

Selecting the appropriate CMS depends on your specific requirements and priorities. Consider the following factors when making a decision:
1. Considerations for Content Creators
- Do you require a user-friendly interface for content editing and previewing?
- Are you looking for a CMS that allows for easy customization and unique design experiences?
- Will you need to deliver content across multiple channels and devices?
- Do you anticipate frequent updates and changes to the content presentation?
2. Considerations for Developers
- Are you seeking the flexibility to choose frontend technologies and frameworks?
- Do you require an API-driven approach to distribute content to various platforms?
- Is future scalability and adaptability important for your project?
- Do you have the necessary technical expertise to develop and maintain custom frontends?
3. Considerations for Marketing Teams
- Do you need the ability to deliver consistent content experiences across multiple channels?
- Are you looking for a CMS that supports personalization and targeting capabilities?
- Does your marketing strategy involve integrating with third-party tools or services?
- Are you interested in leveraging emerging technologies, such as IoT or voice interfaces?
By evaluating your specific needs and considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about whether a Headless CMS or Traditional CMS is the best fit for your requirements.
Case Studies: Headless CMS vs Traditional CMS
To provide you with real-world examples, let’s explore how Headless CMS and Traditional CMS perform in different scenarios:
1. E-commerce Website
A Headless CMS allows an e-commerce website to efficiently manage product information, inventory, and pricing in a centralized backend.
It can easily integrate with various frontend technologies, enabling developers to create immersive shopping experiences on web, mobile, and other channels.
Traditional CMS, on the other hand, offers pre-built e-commerce templates and plugins, making it quicker to set up a basic online store but potentially limiting customization options and scalability.
2. Blogging Platform
For a blogging platform, a Traditional CMS provides an intuitive interface for content creators to write and publish articles.
It offers built-in features like comments, tags, and categories. However, a Headless CMS can offer more flexibility in terms of content distribution.
It allows bloggers to create a custom frontend or integrate with existing blogging platforms while leveraging APIs for content retrieval and management.
3. Mobile Application
When building a mobile application, a Headless CMS shines in delivering content to mobile devices.
It enables developers to fetch content through APIs, ensuring real-time updates and a seamless user experience.
Traditional CMS may struggle to provide the same level of flexibility and performance for mobile apps, as it primarily focuses on web-based content delivery.
Implementing a Headless CMS:

If you decide that a Headless CMS is the right fit for your project, here are some steps to get started:
- Define your content structure and modeling requirements.
- Choose a suitable Headless CMS platform based on your specific needs.
- Develop custom frontends using your preferred technology stack or leverage existing frameworks.
- Connect your frontend applications to the Headless CMS using APIs.
- Test and iterate on the implementation to ensure seamless content delivery.
Popular Headless CMS options include Contentful, Prismic, and Sanity. It’s essential to consider factors such as pricing, scalability, developer friendliness, and community support when selecting a Headless CMS platform.
Migrating from Traditional CMS to Headless CMS
If you’re already using a Traditional CMS and considering a transition to a Headless CMS, here are some key considerations:
- Assess the complexity of your existing website or application and plan the migration process accordingly.
- Identify the content and functionality that needs to be migrated and ensure compatibility with the Headless CMS.
- Develop a migration strategy, including data mapping, content transformation, and redirection plans.
- Execute the migration in a phased manner, testing and validating each step to minimize disruption.
- Train your content creators and developers on the new workflow and tools associated with the Headless CMS.
- Monitor the performance and user feedback post-migration to address any issues and optimize the new system.
Migrating from a Traditional CMS to a Headless CMS requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition while preserving the integrity of your content and functionality.
FAQs about Headless CMS and Traditional CMS:
1. What is the main advantage of a headless CMS?
The main advantage of a headless CMS is its flexibility. It allows for the separation of content from presentation, enabling content to be delivered across multiple platforms and devices through APIs.
2. Can I use a traditional CMS for a mobile app?
While it’s possible to use a traditional CMS for a mobile app, a headless CMS is better suited for mobile applications. It provides the flexibility to fetch and deliver content through APIs, ensuring real-time updates and a smooth mobile experience.
3. Is a headless CMS more expensive than a traditional CMS?
The cost of a CMS depends on various factors, including the specific platform, features, and scalability requirements. While some headless CMS platforms may have higher upfront development costs, the long-term benefits in terms of flexibility and scalability can outweigh the initial investment.
4. How does a headless CMS impact SEO?
A headless CMS doesn’t directly impact SEO. However, it allows for easier implementation of SEO best practices since developers have more control over the frontend code and can optimize it specifically for search engines.
5. Can I switch from a headless CMS to a traditional CMS later on?
Yes, it is possible to switch from a headless CMS to a traditional CMS, although it may involve migrating content and adapting the frontend to the new system. It’s important to evaluate your requirements and future scalability before making such a transition.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of content management, choosing the right CMS is crucial for delivering engaging and seamless experiences to your audience. Understanding the differences between Headless CMS and Traditional CMS is key to making an informed decision.
Headless CMS provides flexibility, scalability, and multi-channel content delivery, making it ideal for organizations that require diverse digital touchpoints. Traditional CMS offers user-friendly interfaces, quick website setup, and integrated content presentation, making it suitable for simpler projects with fewer distribution requirements.
Consider your specific needs, the nature of your content, and the desired user experiences when selecting a CMS. Assess the pros and cons, evaluate case studies, and consider the perspectives of content creators, developers, and marketing teams. This will help you determine the best fit for your organization.
Remember, implementing a CMS is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires careful planning, testing, and ongoing optimization to ensure that your chosen CMS aligns with your business goals and enables you to create and deliver content effectively.
With the right CMS in place, you can streamline your content management processes, enhance collaboration, and provide engaging experiences to your audience across multiple platforms and devices.